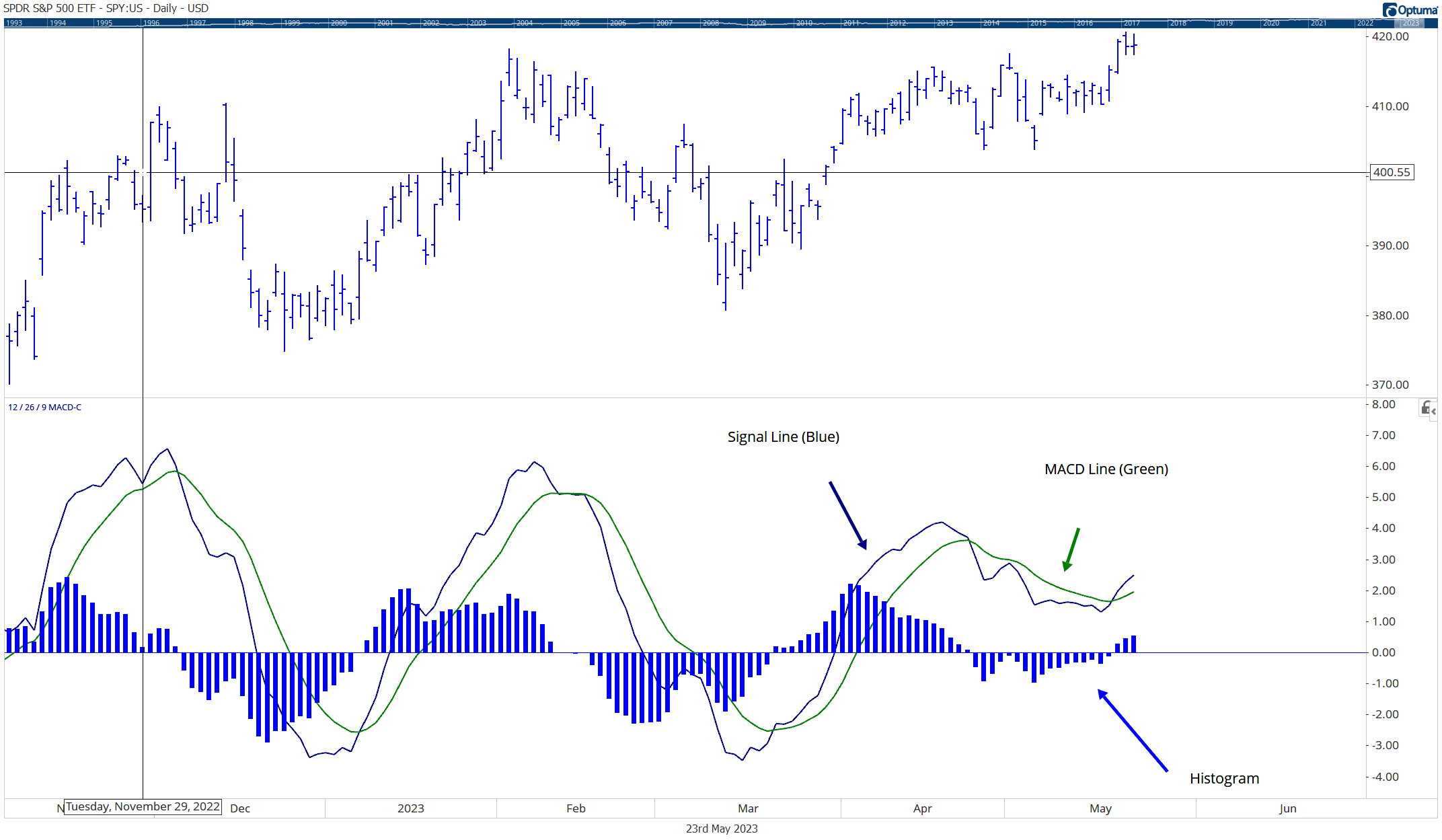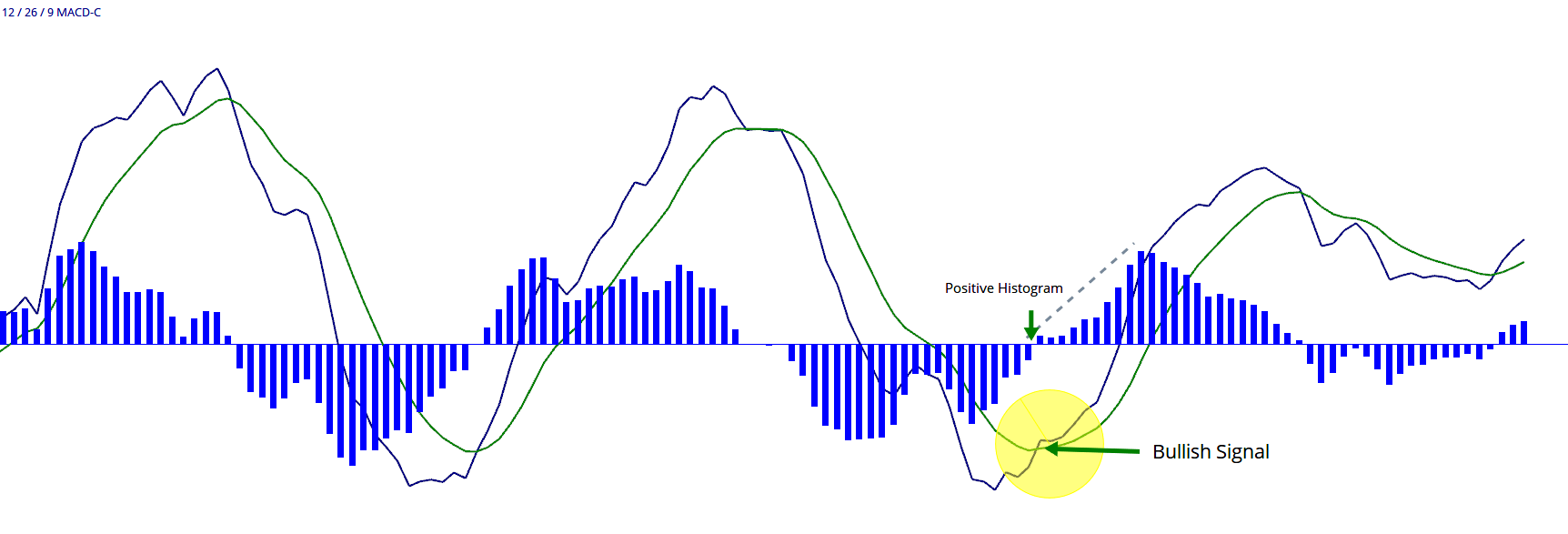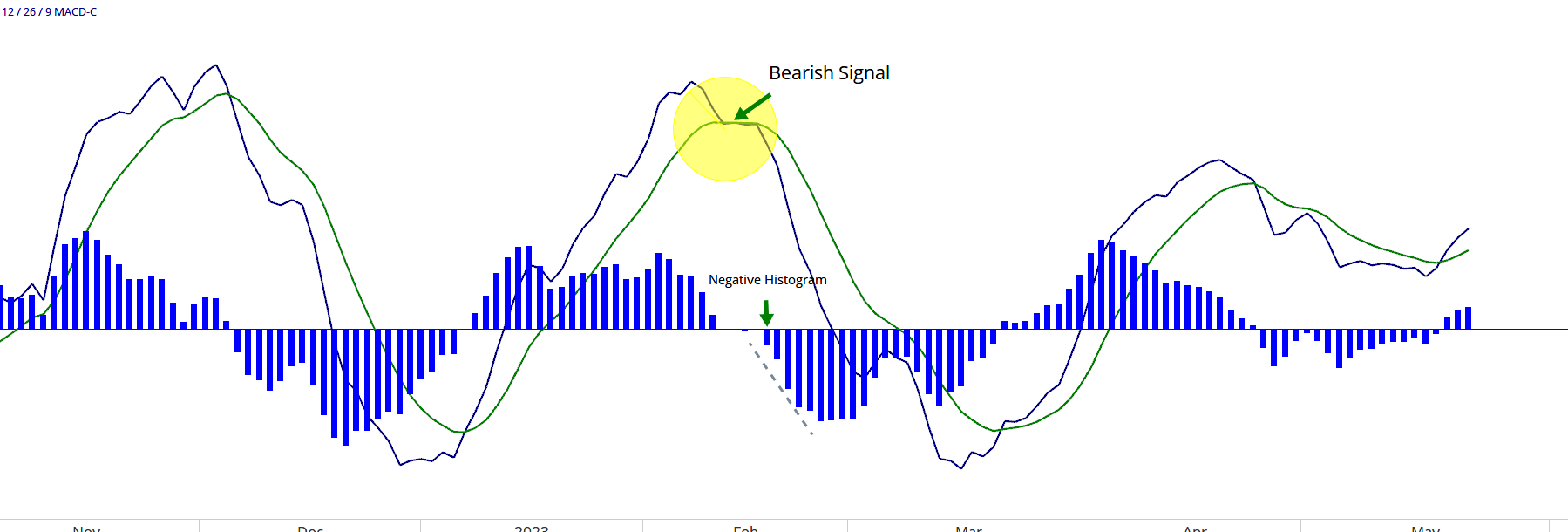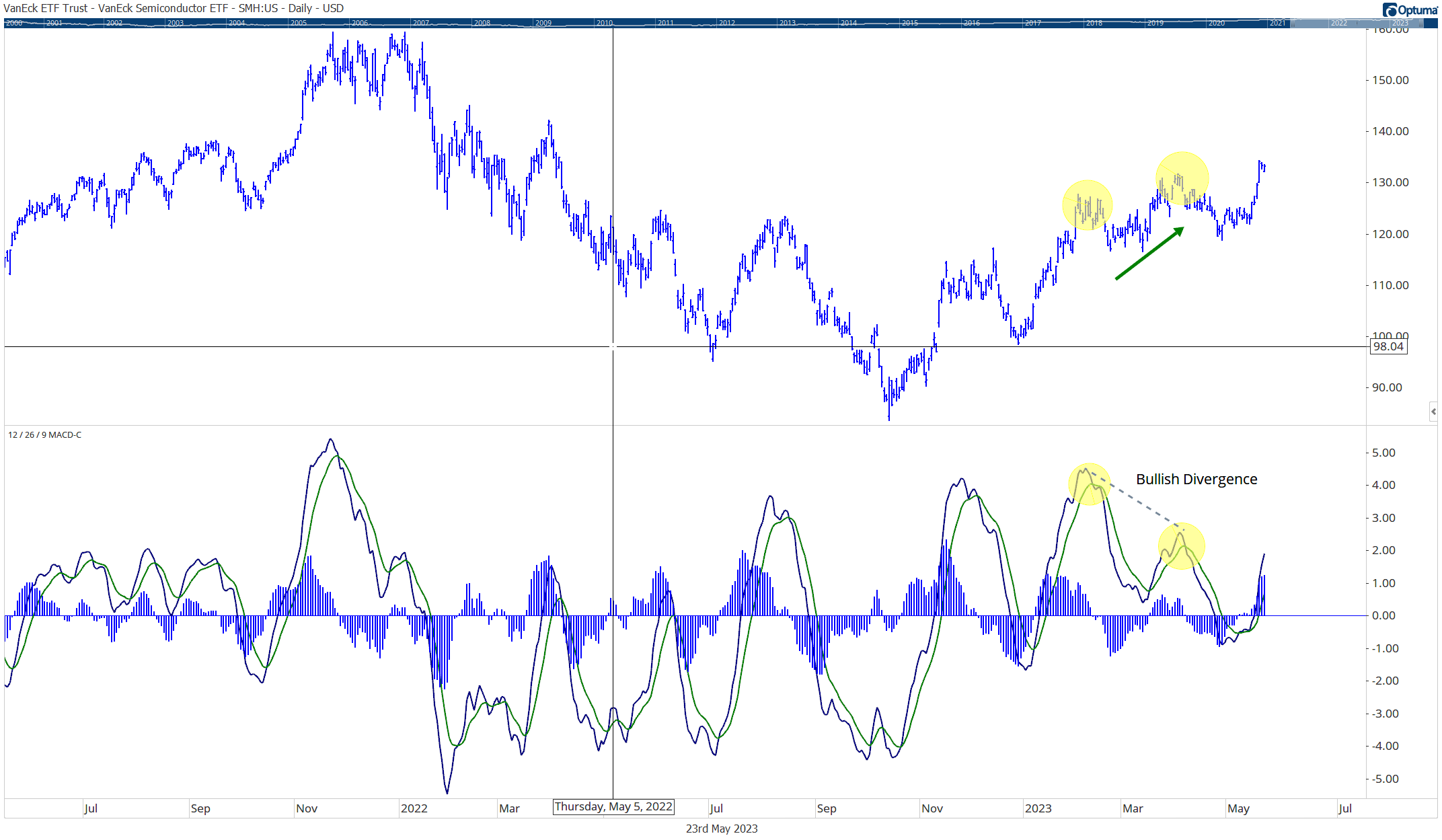
Momentum Investing Research: Harnessing the Power of Market Trends
Momentum investing research has proven time and time again that strategies involving the purchasing of stocks or other securities demonstrating high returns over the past three to twelve months have added alpha over traditional buy-and-hold investment strategies.
This tactic has been leveraged by both professional investors and individual traders for many years, helping many to consistently outperform the stock market.
In this article, we will delve into the world of momentum investing research, exploring what it is, how it operates, and why it has been so successful.
What is Momentum Investing?
Momentum investing is a systematic investment approach that capitalizes on the continuance of existing market trends. This method entails buying securities that have exhibited an upward price trend and selling those with a downward trend. It operates on the assumption that securities that have performed well in the past will continue to excel, and those that have underperformed will continue to do poorly.
The concept of momentum investing is deeply rooted in behavioral finance, attributing its effectiveness to cognitive biases among investors. Investors can be slow to react to new information, leading to trends persisting for longer than traditional financial models might suggest. Likewise, investor sentiment and herd behavior can further perpetuate these trends.
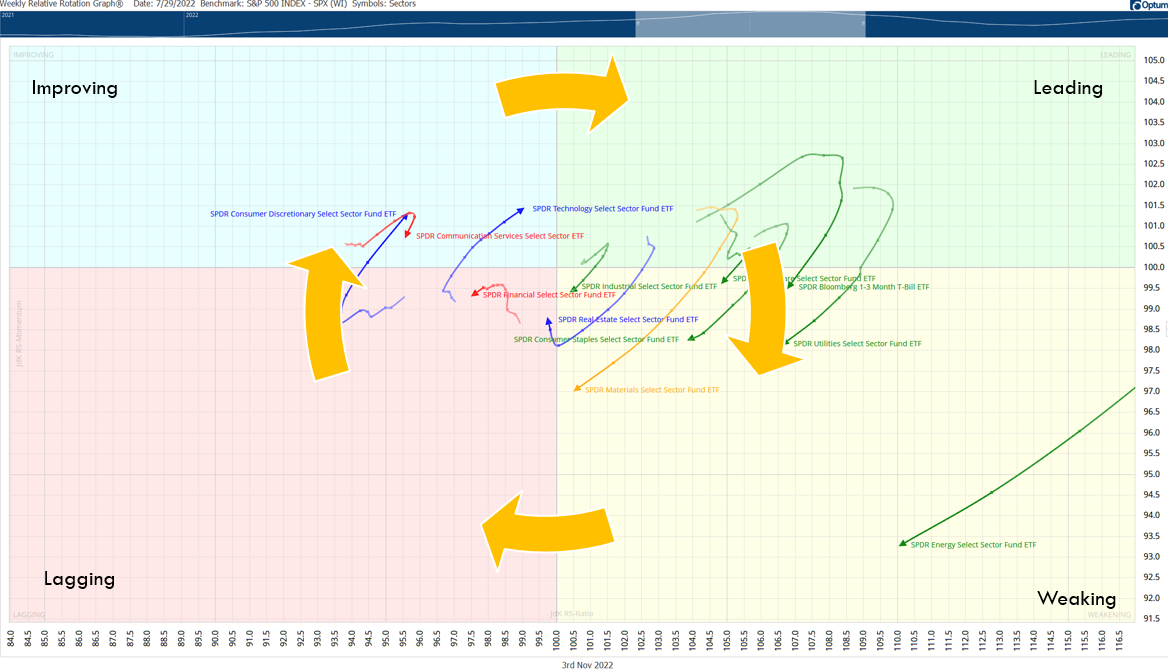
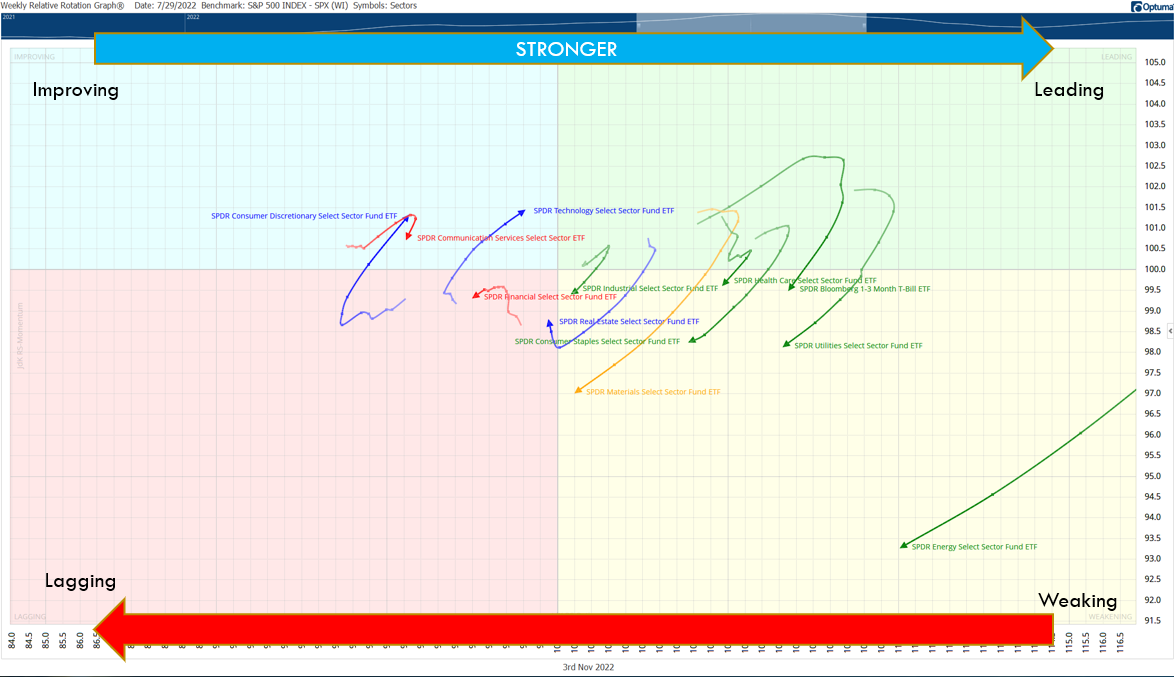
Momentum investing necessitates active monitoring and reevaluation of market trends. Investors must frequently rebalance their portfolios, often on a monthly or quarterly basis, to maintain exposure to securities currently demonstrating strong momentum.
In contrast to ‘buy and hold’ strategies, momentum investing adopts a more dynamic approach, continually adjusting to the ebb and flow of market trends. This strategy can be applied to individual stocks, industry sectors, or even entire markets, and it can be utilized across various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies.
Why Has Momentum Investing Outperformed The Stock Market?
Historical data and academic research demonstrate the effectiveness of momentum investing. For instance, a comprehensive study by Jegadeesh and Titman (1993) found that strategies that bought stocks that had performed well in the past and sold stocks that had performed poorly generated significant positive returns over 3- to 12-month holding periods.
Furthermore, a research paper by Moskowitz, Ooi, and Pedersen (2012) analyzed momentum returns across different asset classes and found consistent momentum premiums.
These researchers also discovered that momentum strategies implemented across various asset classes provided significant diversification benefits.
Table: Momentum Premiums Across Asset Classes (Moskowitz, Ooi, and Pedersen, 2012)
| Asset Class | Annualized Momentum Premium |
| Equities | 7.6% |
| Bonds | 7.0% |
| Commodities | 9.8% |
| Currencies | 8.1% |
As evidenced by the table, the momentum premium – the additional return obtained from a momentum strategy compared to a benchmark – is significant across different asset classes.
In the academic world, the pioneering research on momentum was a 1993 study published in the Journal of Finance by Narasimhan Jegadeesh and Sheridan Titman, both at UCLA Anderson at the time. They documented how strategies of buying recent stock winners and selling recent losers generated significantly higher near-term returns than the U.S. market overall from 1965 to 1989.
The authors established the basic time frame for momentum-investing success as a three-to-12-month window on either side. In other words, a stock’s relative performance over the previous three to 12 months typically predicted its relative performance for the following three to 12 months.
They measured various time combinations of prior returns and future returns within those windows and found trading them to be “on average quite profitable” strategies.
For example, a portfolio that selected stocks based on their previous six-month returns, and then held them for six months, generated an extra return of about 1 percent per month above what would have been expected.
Data Analysis & Examples Of Momentum Investing RESEARCH
There’s a good reason for academics to want to nail down the key factor behind momentum’s success: As an investment strategy, it’s a thumb in the eye of the “efficient market hypothesis” (EMH), one of the central tenets of modern finance.
EMH, developed by the economist Eugene Fama in the 1960s, holds that a stock’s price at any moment reflects all of the relevant information about the company. So it’s impossible to ferret out a bargain because investors are rational beings and share prices are always exactly what they “should” be, given what investors collectively know.
That, of course, is the argument that has made index (or “passive”) stock investing so incredibly popular over the last 20 years: You can’t outsmart the market, so just own the whole thing.
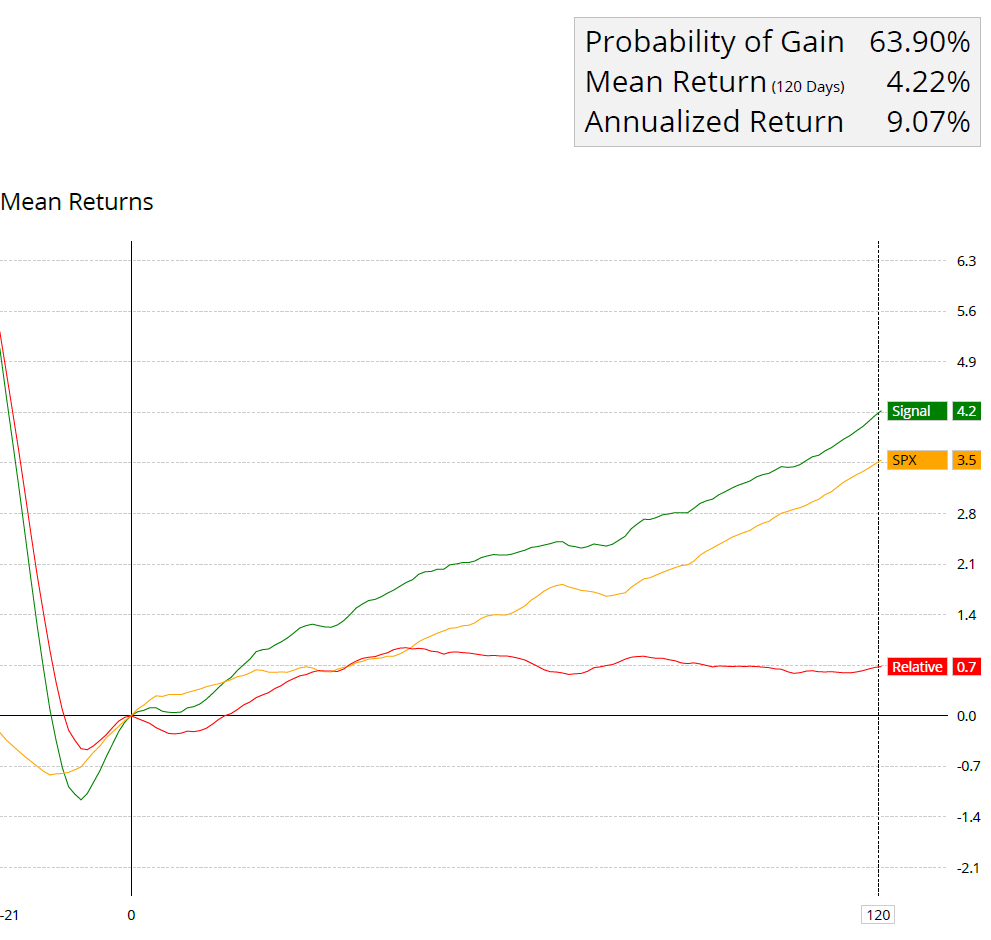
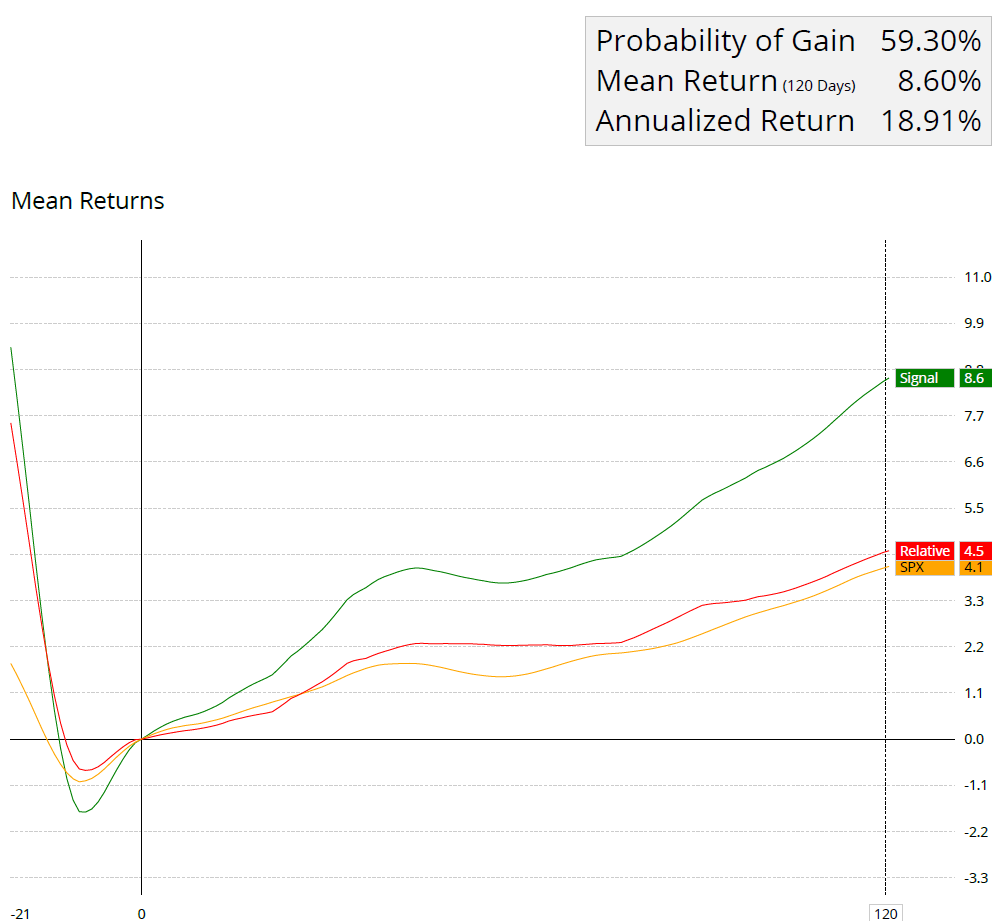
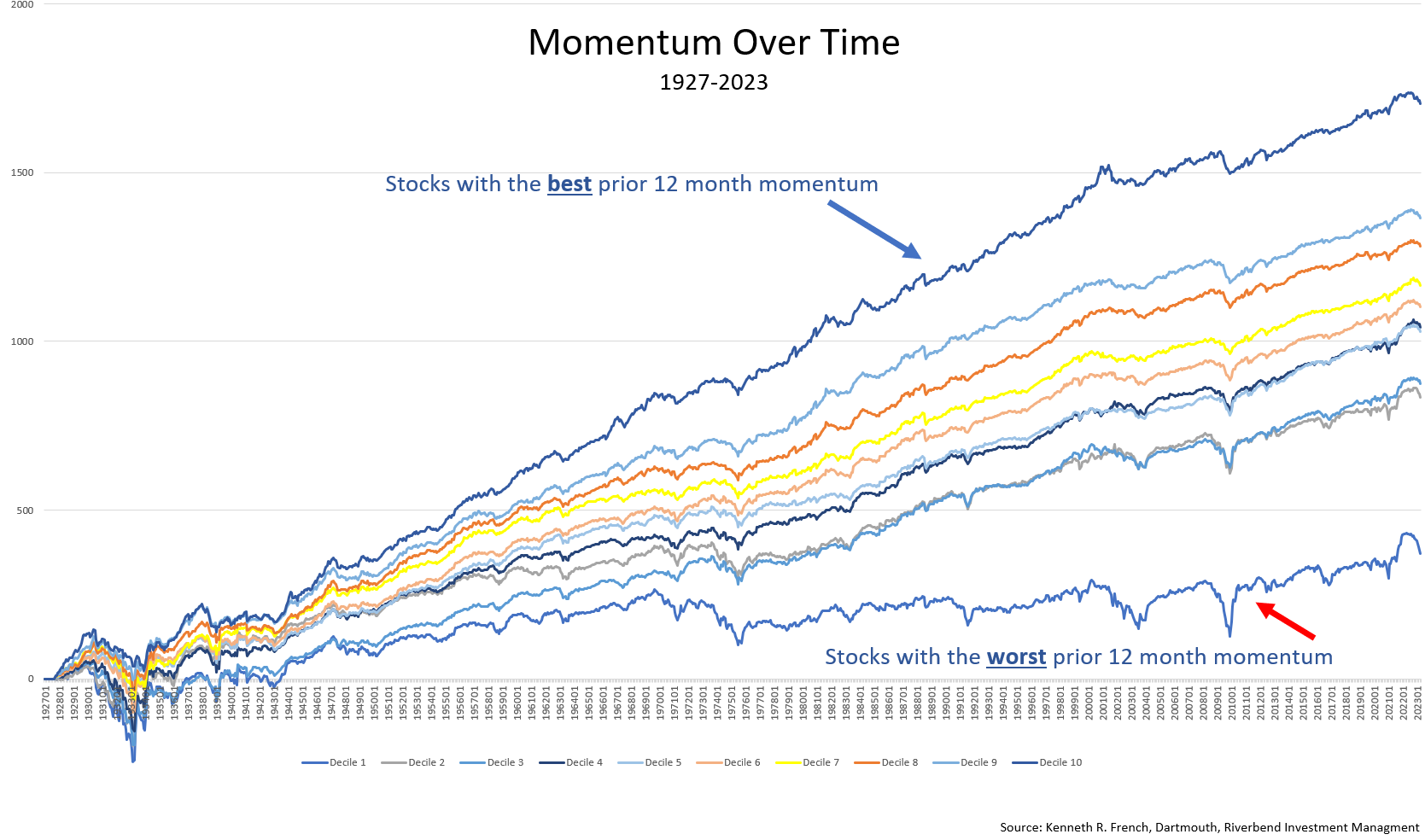
To illustrate how effective momentum investing can be compared with traditional long-term strategies, let’s examine some data analysis examples below:
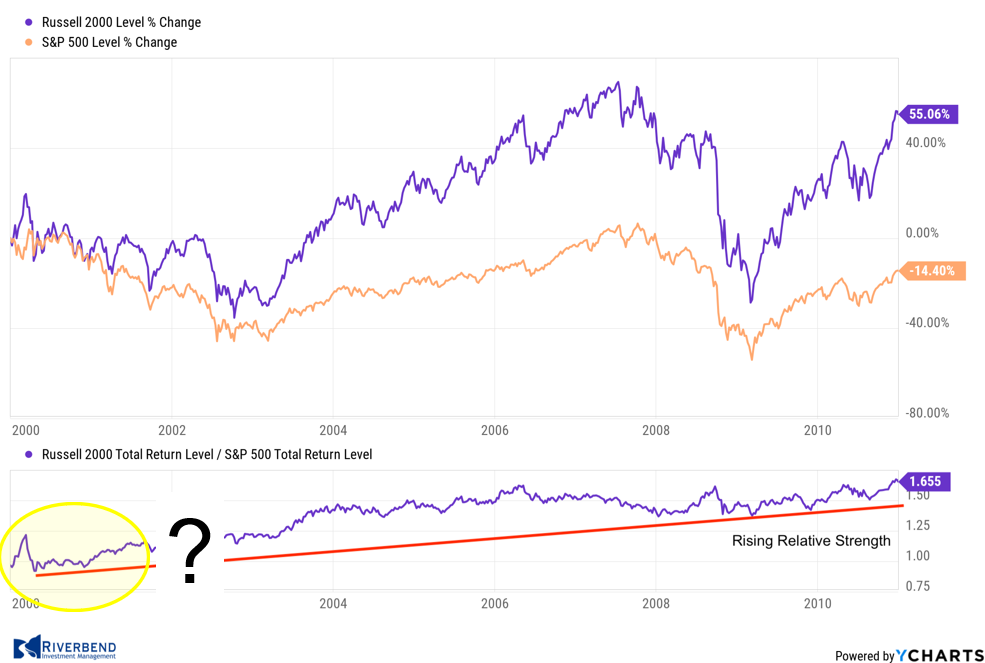
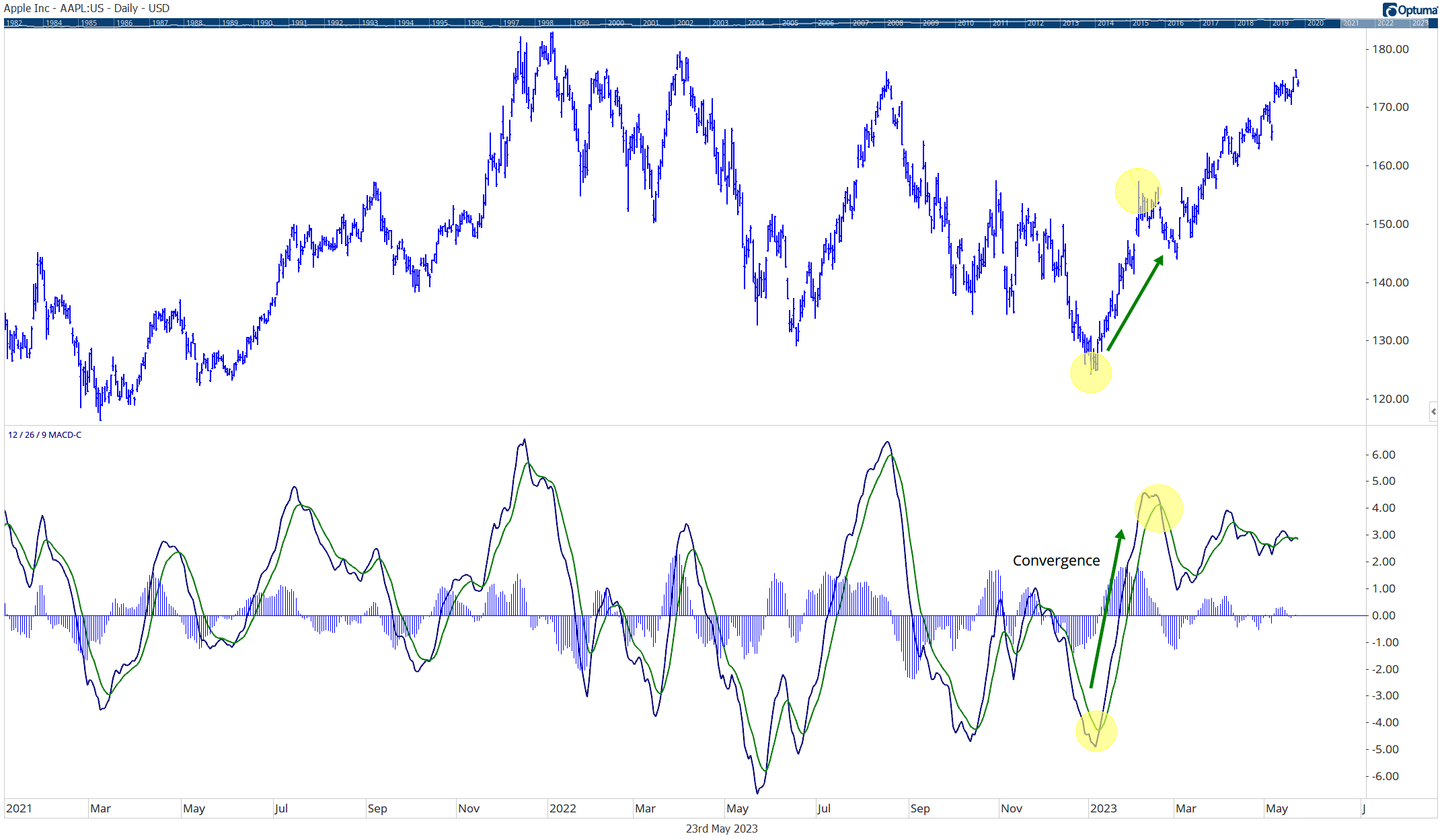
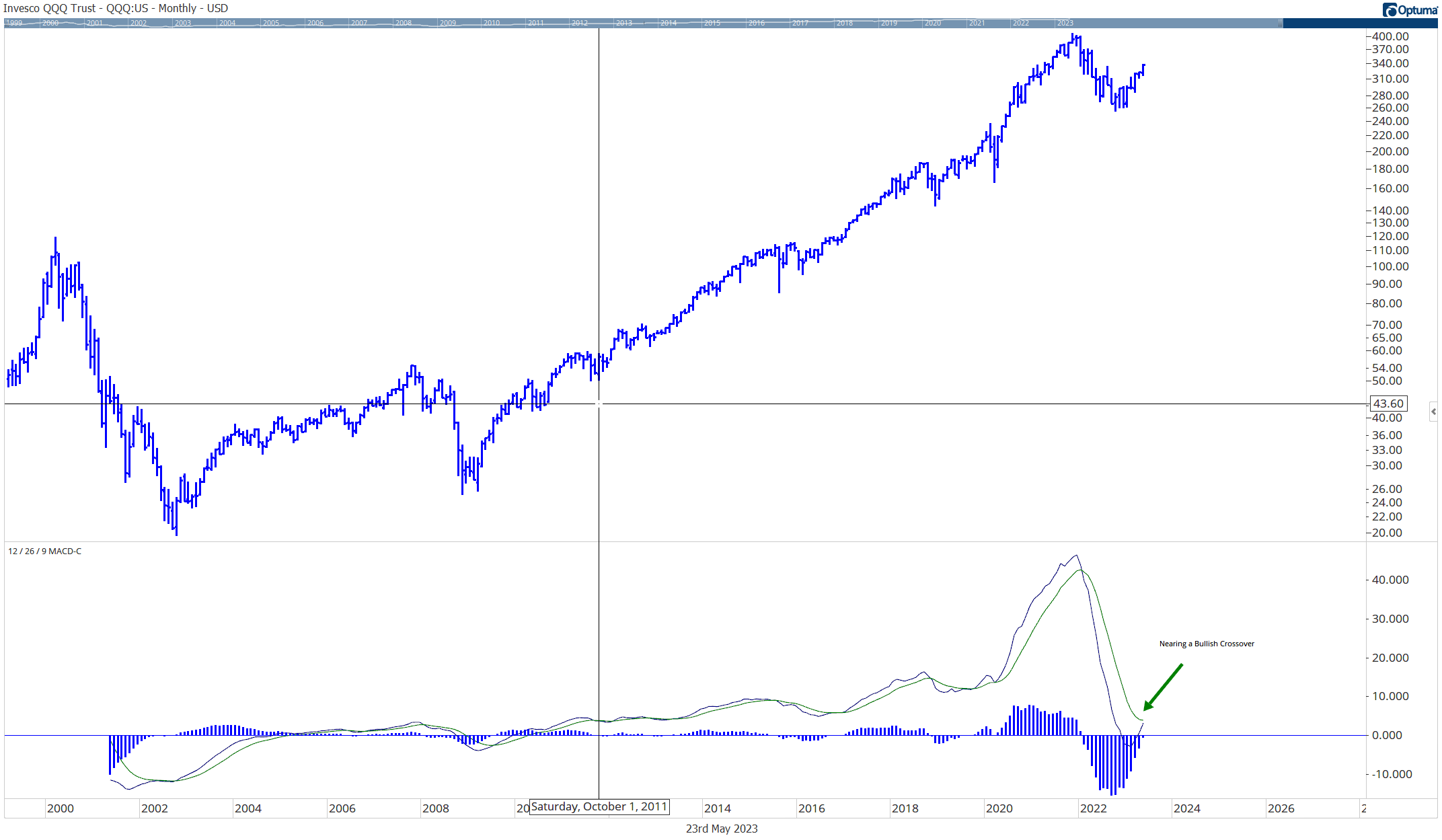
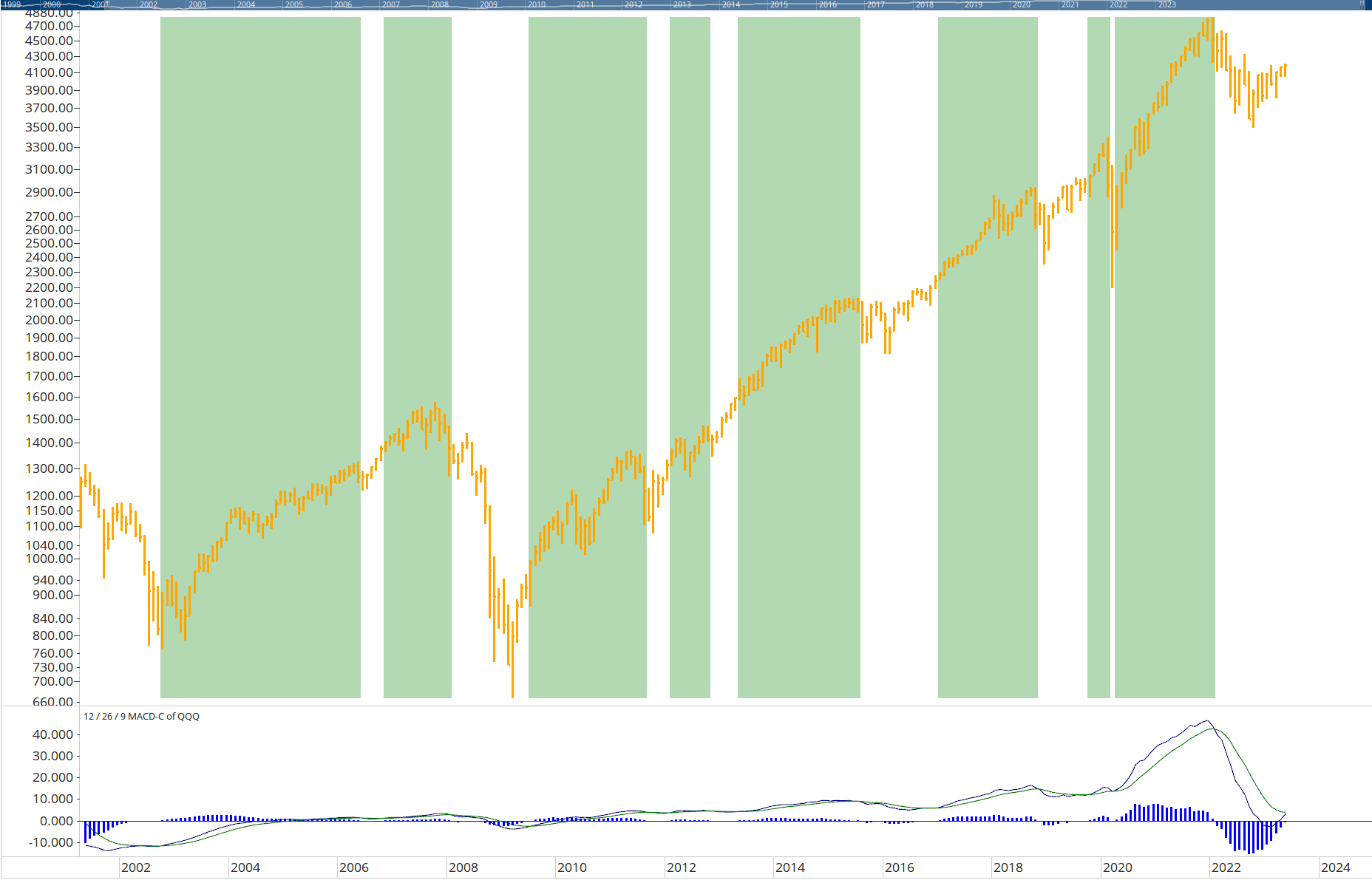
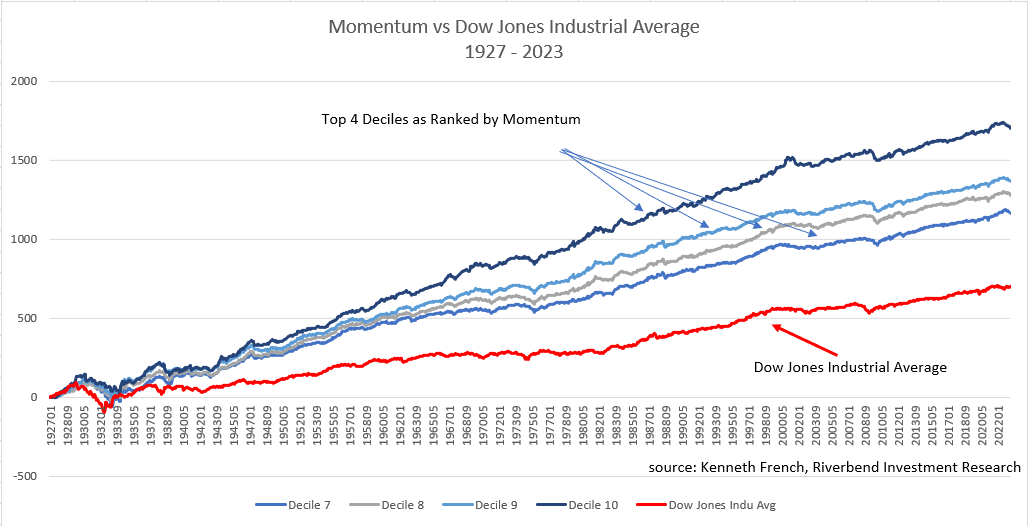
The above graph shows the difference in returns from January 1927 to January 2023 between the top 4 momentum ranked deciles compared to the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
This simple chart demonstrates that momentum investing historically has outperformed traditional buy & hold strategies over time.
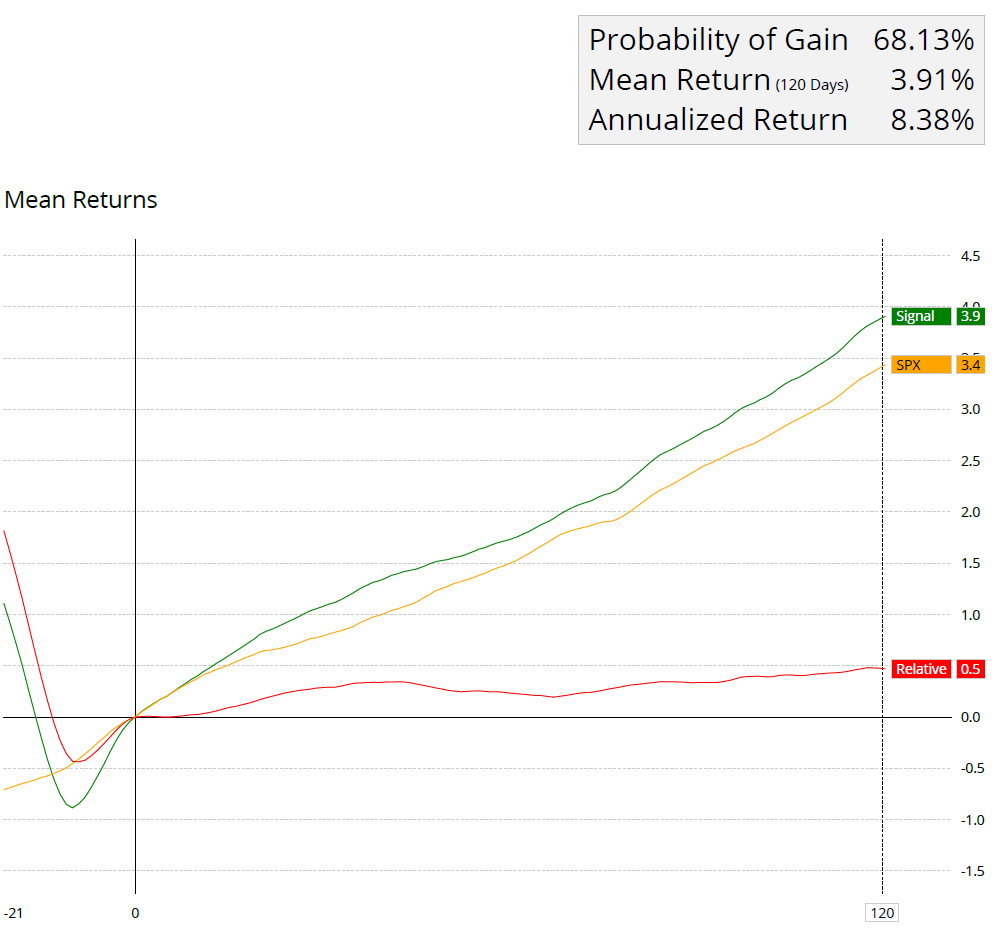
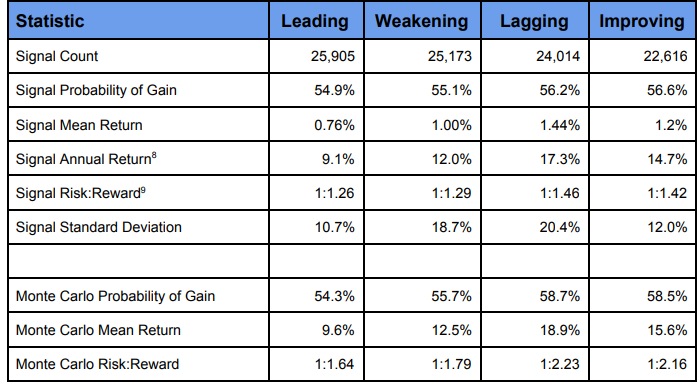
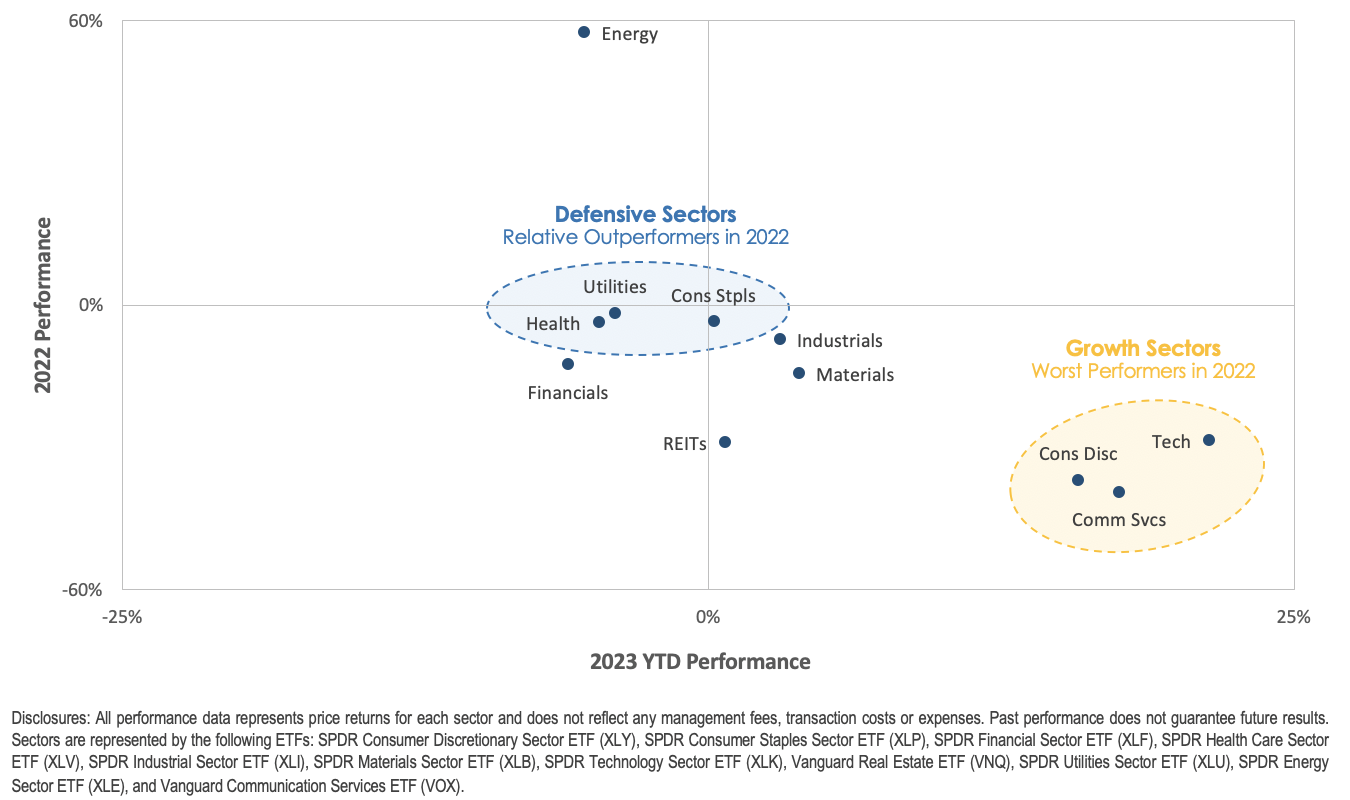
We can also look at further examples of how momentum investing has outperformed traditional strategies over time: one example comes from research conducted by Anderson Review which found that “stocks where past returns accumulate gradually exhibit more momentum than stocks where returns are accumulated in a lumpy fashion” – meaning that gradual increases in prices tend to lead to further gains while sudden spikes tend not lead anywhere significant in terms of profitability over time; another example comes from research conducted by Quantpedia which found that “momentum factor effect” was present across all asset classes studied – meaning that even when markets were volatile overall, there were still opportunities for making profits through careful selection of stocks based on their recent performance; finally, research conducted by Research Affiliates which showed “simulated portfolios based on momentum add remarkable value” even during periods when markets were down overall – showing us how powerful this strategy can be even during difficult times for markets overall.
Study after study has shown that momentum investing typically is a market-beating strategy. So how has that translated into real-world results?
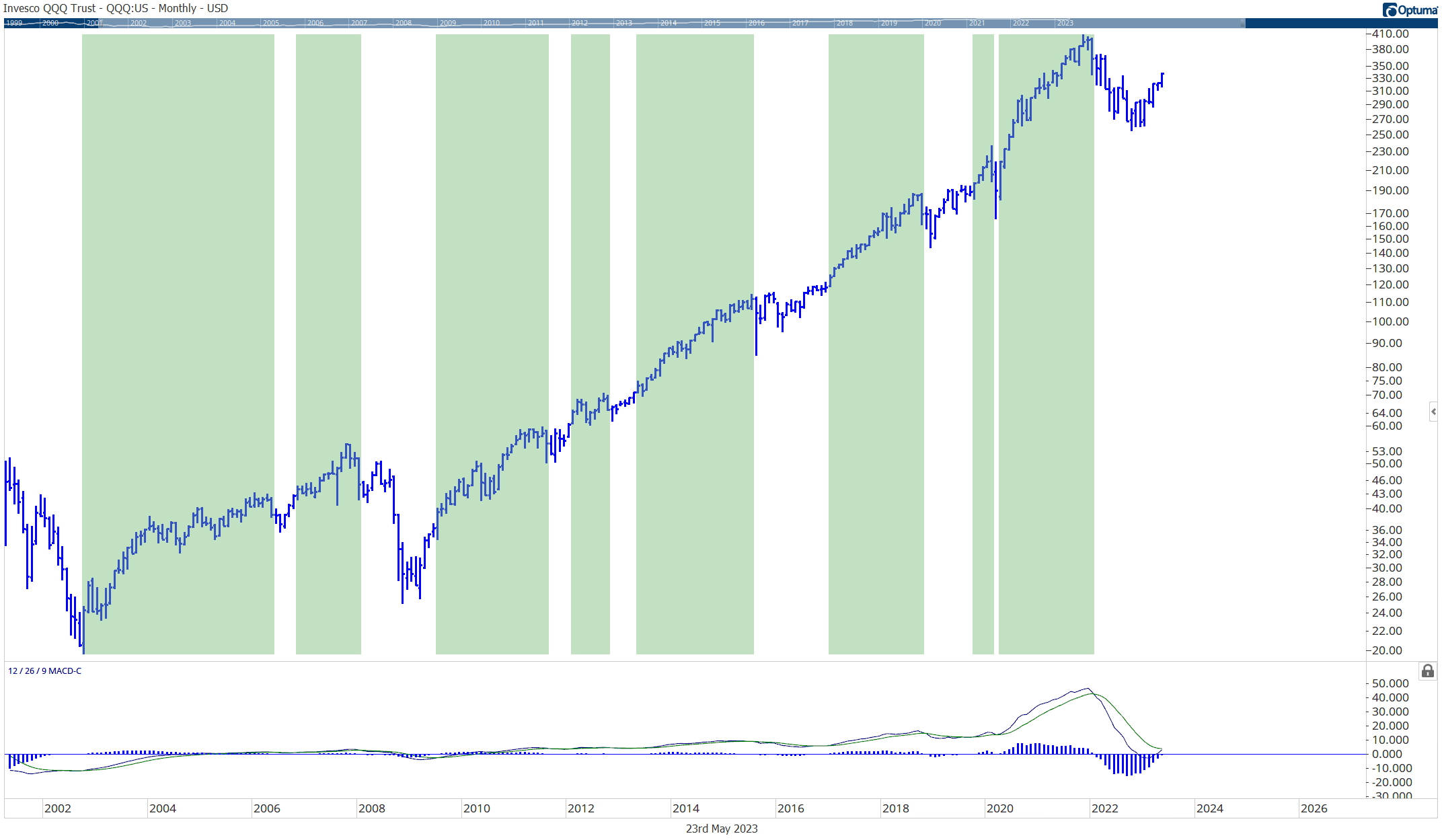
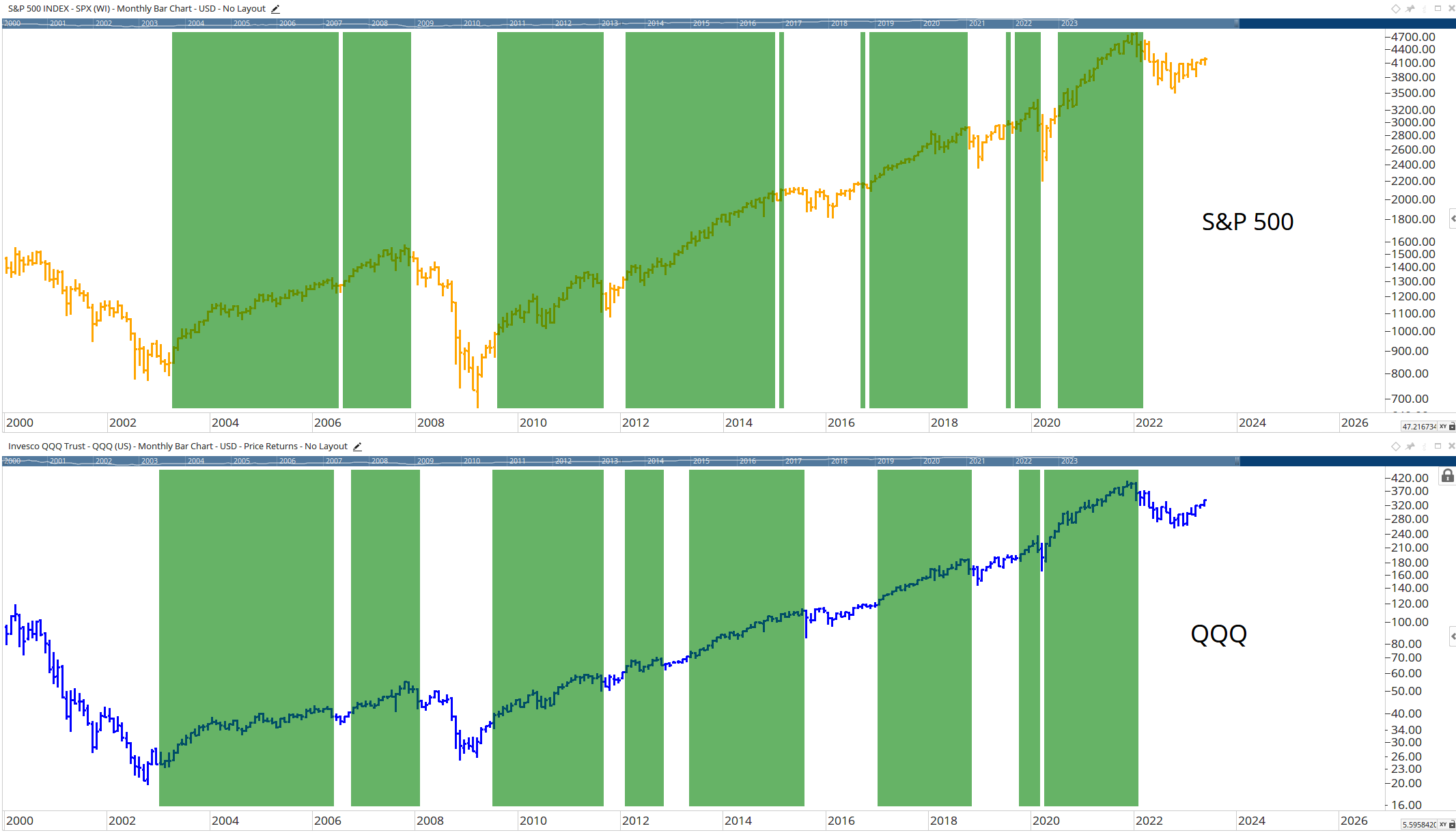
Consider the iShares Edge MSCI USA Momentum Factor exchange-traded fund (ticker symbol: MTUM). Launched in 2013, the fund has grown to $10 billion in assets by outperforming the benchmark Standard & Poor’s 500 index.
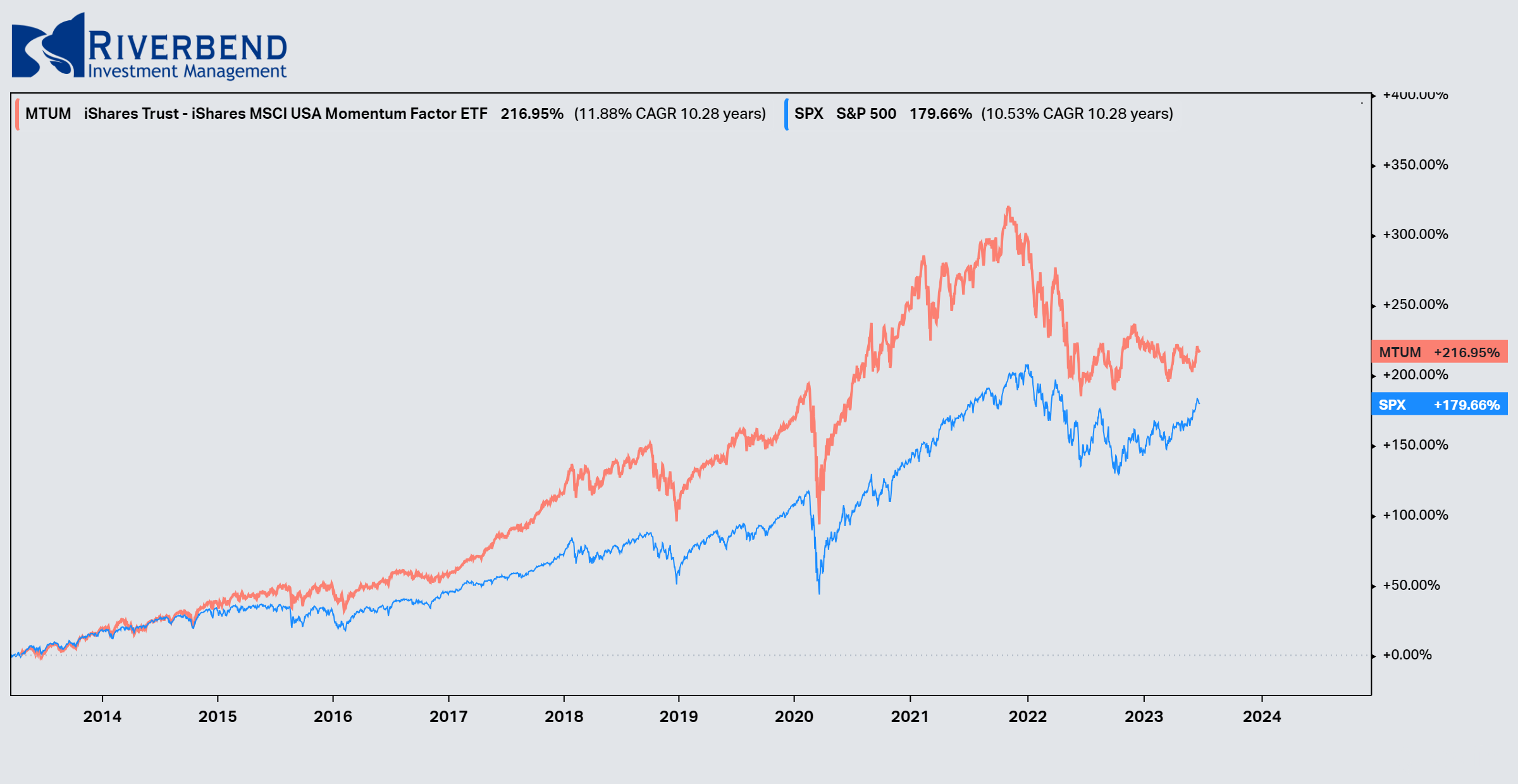
source: Koyfin
The fund is designed to track the MSCI USA Momentum Index, which comprises the recent best-performing U.S. large- and mid-capitalization stocks.
The fundamentals of the companies don’t matter; the stocks just have to be market leaders to get into the index (and the fund).
To identify the leaders, each of the 675 stocks in the broad MSCI USA market index is given a “momentum value” based on performance over the recent six months and the recent 12 months. The momentum values then are risk-adjusted to give each stock a momentum score. The 120 or so highest-scoring stocks then make up the index. Twice a year the index — and the fund — are reconstituted to pick up new market leaders and sell those that have slumped out.
Conclusion
In conclusion, momentum investing research has revealed why this approach has become so popular among both professional investors and individual traders alike: it takes advantage of market trends to generate consistent profits while reducing risk compared with traditional buy & hold strategies.
Furthermore, we can see from our data analysis examples above just how effective this strategy has been historically compared with traditional approaches, leading us to believe it will continue to outperform going forward.
Combined with other tools, such as risk management, momentum investing can be a powerful addition to an investor’s tool kit.
John Rothe, CMT
June 2023
References:
- Jegadeesh, N., & Titman, S. (1993). Returns to buying winners and selling losers: Implications for stock market efficiency. The Journal of Finance, 48(1), 65-91.
- Moskowitz, T. J., Ooi, Y. H., & Pedersen, L. H. (2012). Time series momentum. Journal of Financial Economics, 104(2), 228-250.
- https://alphaarchitect.com/category/architect-academic-insights/factor-investing/momentum-investing/
- https://anderson-review.ucla
- Kenneth R. French http://mba.tuck.dartmouth.edu/pages/faculty/ken.french/index.html
- https://www.iShares.com
- https://www.Koyfin.com
John Rothe
HAS BEEN FEATURED IN:









The opinions expressed on this site are those solely of John Rothe and do not necessarily represent those of Riverbend Investment Management LLC (Riverbend). This website is made available for educational and entertainment purposes only. Mr. Rothe is an Investment Adviser Representative of Riverbend. This website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a complete description of the investment services or performance of Riverbend. Nothing on this website should be interpreted to state or imply that past results are an indication of future performance. A copy of Riverbend’s Part II of Form ADV and privacy policy is available upon request. This website is in no way a solicitation or an offer to sell securities or investment advisory services. Mr. Rothe and Riverbend Investment Management LLC (Riverbend) disclaim responsibility for updating information. In addition, Mr. Rothe, and Riverbend disclaim responsibility for third-party content, including information accessed through hyperlinks.